Apocryphal but still quotable.
 That’s how Britain’s venerable broadcaster, the BBC, treated the mythical anecdote about media titan William Randolph Hearst and his purported vow to “furnish the war” with Spain in the late 19th century.
That’s how Britain’s venerable broadcaster, the BBC, treated the mythical anecdote about media titan William Randolph Hearst and his purported vow to “furnish the war” with Spain in the late 19th century.
In an article posted online yesterday, the BBC described Hearst as the “definitive [news] baron” and declared:
“He’s credited with the invention of tabloid journalism in the 1890s when his New York Journal began a bitter circulation war with Joseph Pulitzer’s New York World. He also had a reputation as a warmonger.
“‘You furnish the pictures and I’ll furnish the war,’ goes an apocryphal instruction he was supposed to have sent in a telegram to an illustrator in Havana.”
That’s right, the line is apocryphal. What, then, is the point in using it? As a none-too-clever, back-handed way of buttressing the dubious notion that Hearst and his newspapers were capable of fomenting a war?
That’s sloppy journalism from a leading international news organization.
As I discuss in my latest book, Getting It Wrong, Hearst’s purported vow to “furnish the war” with Spain is a particularly tenacious media-driven myth — a prominent but dubious tale about journalism that masquerades as factual.
I note that the tale about Hearst’s vow “has achieved unique status as an adaptable, hardy, all-purpose anecdote, useful in illustrating any number of media sins and shortcomings.
“It has been invoked to illustrate the media’s willingness to compromise impartiality, promote political agendas, and indulge in sensationalism. It has been used, more broadly, to suggest the media’s capacity to inject malign influence into international affairs.”
Reasons for doubting the presumptive Hearstian vow are many, I point out in Getting It Wrong, and include the fact that the telegram in which Hearst supposedly made the statement — in an exchange with the artist Frederic Remington, on assignment to Cuba — has never turned up.
Plus, Hearst denied making such a vow.
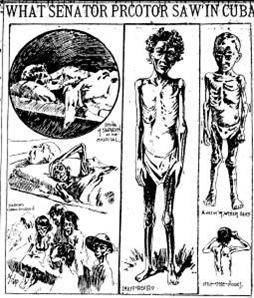
Not only that, but the anecdote lives on lives on despite what I call “an irreconcilable internal inconsistency.” That is, it would have been absurd for Hearst to vow to “furnish the war” because war— specifically, the Cuban rebellion against Spanish colonial rule— was the reason he sent Remington to Cuba in the first place.
The artist was in Cuba for just six days in January 1897. By that time, the Cuban rebellion — a war for political independence — had reached islandwide proportions. “Anyone reading U.S. newspapers in early 1897 would have been well aware that Cuba was a theater of a nasty war,” I write in Getting It Wrong.
Given the context, Hearst’s purported vow is utterly illogical.
And to invoke the anecdote knowing that it’s apocryphal is little short of disingenuous.
The BBC’s reference to Hearst’s being “credited with the invention of tabloid journalism in the 1890s” also is questionable.
Hearst’s style of flamboyant journalism certainly helped inspire the epithet “yellow journalism,” but he was no father of tabloid journalism.
If anything, Hearst was a latecomer to that genre.
As David Nasaw wrote in The Chief, his admirably even-handed biography of Hearst, the press baron didn’t embrace the tabloid until the 1920s “because he was not comfortable with the format.
“He had no interest in publishing a picture newspaper that had little room for political coverage, columns, cartoons, and the editorials he cared so much about.”
Many thanks to Instapundit
Glenn Reynolds for linking to this post.
Recent and related:
- ‘News of World’ closure breaks link to 19th century yellow journalism
- Yellow journalism ‘brought about Spanish-American War’? But how?
- The ‘anniversary’ of a media myth: ‘I’ll furnish the war’
- As if Hearst ‘were back with us,’ vowing to ‘furnish the war’
- ‘Famously rumored’: Hearst and his reputed vow
- Those delicious but phony quotes ‘that refuse to die’
- More than merely sensational
- Media myths, the junk food of journalism
- ‘A debunker’s work is never done’
- ‘Getting It Wrong’ goes on Q-and-A